Website-Einstellungen
Produkte
Produkte
Leistung
HF
Transformatoren
Tools für Design-Support
Nutzen Sie unsere ‚Suite of Tools‘ für die Auswahl, die Analyse und den Vergleich von Induktivitäten
Alle Tools anzeigen
Parametrische Suche
Lassen Sie sich die Liste unserer Induktivitäten und Filter zu Ihren Parametern anzeigen.
Erforschen
Datenblätter
Sie suchen nach einem Datenblatt? Suchen Sie nach Produkt und laden Sie das PDF herunter
Liste anzeigen
Automobiltechnik
Informationsmaterial
![YouTube preview image]()
![YouTube preview image]()
![YouTube preview image]()
![YouTube preview image]()
Informationsmaterial
Produktdokumentation
Handhabung und Verarbeitung
Modelle und Layout-Tools
Kurse/Schulung
Video-Bibliothek

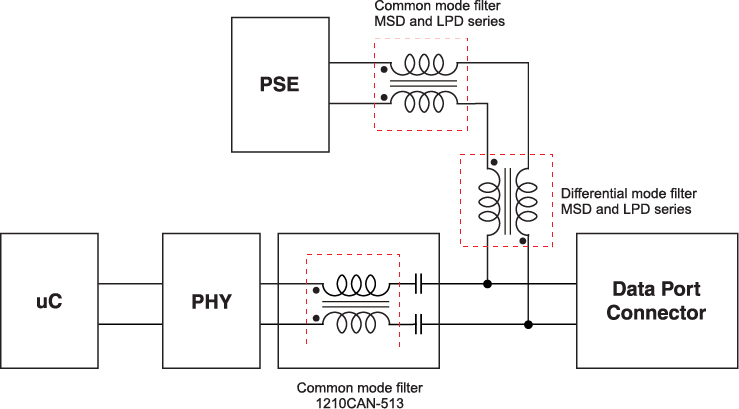
Cx Family Common Mode Chokes
0402CT Low Profile Chip Inductors

XAL7050 High-inductance Shielded Power Inductors

XGL4020 Ultra-low DCR Power Inductors
Student Support
Learn more about magnetics, request free samples or ask our engineers a question.
Get Support
Quality
Quality
Qualitätszertifizierung
Materialzertifizierung
Sicherheitszertifizierung
Zuverlässigkeit
Handhabung / Verarbeitung
Über
Über
Über
Jobs
Standorte
Informationsmaterial

.jpg)